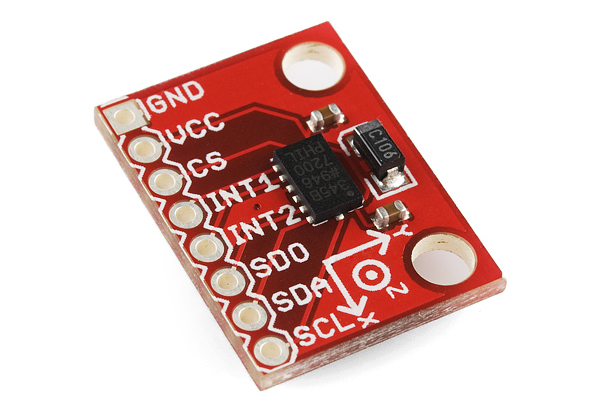
■關於 ADXL345:(摘錄於 ADI 官方網頁)
ADXL345是一款小巧纖薄的低功耗三軸加速度計,可以對高達±16 g的加速度進行高分辨率(13位)測量。數字輸出數據為16位二進制補碼格式,可通過SPI(3線或4線)或者I2C 數字接口訪問。
ADXL345非常適合移動設備應用。它可以在傾斜檢測應用中測量靜態重力加速度,還可以測量運動或衝擊導致的動態加速度。它具有高分辨率(4 mg/LSB),能夠測量約0.25°的傾角變化。使用ADXL345等數字輸出加速度計時,無需進行模數轉換,從而可以節省系統成本和電路板面積。此外,ADXL345內置多種功能。活動/非活動檢測、單擊/雙擊檢測以及自由落體檢測均在內部完成,無需主機處理器執行任何計算。內置32級FIFO存儲緩衝器可以減輕主機處理器的負擔,起到簡化算法和省電的作用。利用內置的活動/非活動檢測功能,將ADXL345用作“運動開關”(無活動時關閉整個系統,檢測到活動時才開啟),系統可以實現進一步省電。
■關於接線:圖左側為 SPI 四線式接線方法(SPI 三線式接線則省略SDO不接),圖右側為 I2C 接線方法(Rp=10K Ohm)。
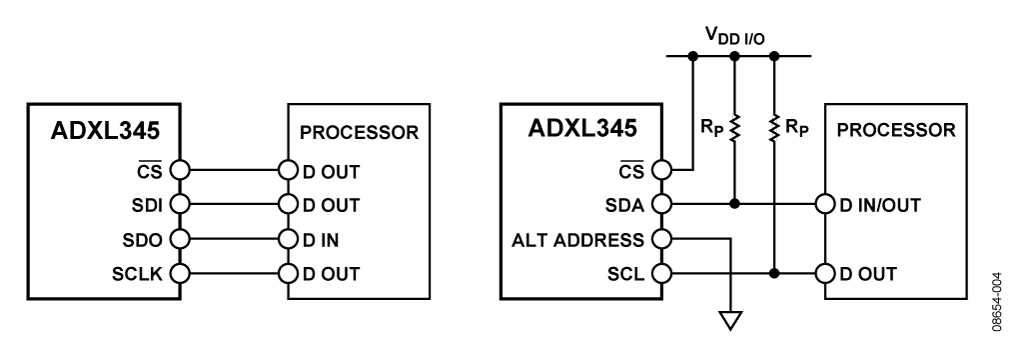
補充:引腳名稱有很多叫法(或標示)但他們都是相同。
- SDA/SDI/SDIO
- SDO/ALT ADDRESS
- SCL/SCLK
■關於程式:(以下提供 Arduino Code)
程式一:使用 SPI 連接(四線式)(摘錄於:https://www.sparkfun.com/tutorials/240)
//Add the SPI library so we can communicate with the ADXL345 sensor
#include <SPI.h>
//Assign the Chip Select signal to pin 10.
int CS=10;
//This is a list of some of the registers available on the ADXL345.
//To learn more about these and the rest of the registers on the ADXL345, read the datasheet!
char POWER_CTL = 0x2D; //Power Control Register
char DATA_FORMAT = 0x31;
char DATAX0 = 0x32; //X-Axis Data 0
char DATAX1 = 0x33; //X-Axis Data 1
char DATAY0 = 0x34; //Y-Axis Data 0
char DATAY1 = 0x35; //Y-Axis Data 1
char DATAZ0 = 0x36; //Z-Axis Data 0
char DATAZ1 = 0x37; //Z-Axis Data 1
//This buffer will hold values read from the ADXL345 registers.
char values[10];
//These variables will be used to hold the x,y and z axis accelerometer values.
int x,y,z;
void setup(){
//Initiate an SPI communication instance.
SPI.begin();
//Configure the SPI connection for the ADXL345.
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3);
//Create a serial connection to display the data on the terminal.
Serial.begin(9600);
//Set up the Chip Select pin to be an output from the Arduino.
pinMode(CS, OUTPUT);
//Before communication starts, the Chip Select pin needs to be set high.
digitalWrite(CS, HIGH);
//Put the ADXL345 into +/- 4G range by writing the value 0x01 to the DATA_FORMAT register.
writeRegister(DATA_FORMAT, 0x01);
//Put the ADXL345 into Measurement Mode by writing 0x08 to the POWER_CTL register.
writeRegister(POWER_CTL, 0x08); //Measurement mode
}
void loop(){
//Reading 6 bytes of data starting at register DATAX0 will retrieve the x,y and z acceleration values from the ADXL345.
//The results of the read operation will get stored to the values[] buffer.
readRegister(DATAX0, 6, values);
//The ADXL345 gives 10-bit acceleration values, but they are stored as bytes (8-bits). To get the full value, two bytes must be combined for each axis.
//The X value is stored in values[0] and values[1].
x = ((int)values[1]<<8)|(int)values[0];
//The Y value is stored in values[2] and values[3].
y = ((int)values[3]<<8)|(int)values[2];
//The Z value is stored in values[4] and values[5].
z = ((int)values[5]<<8)|(int)values[4];
//Print the results to the terminal.
Serial.print(x, DEC);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.print(y, DEC);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.println(z, DEC);
delay(10);
}
//This function will write a value to a register on the ADXL345.
//Parameters:
// char registerAddress - The register to write a value to
// char value - The value to be written to the specified register.
void writeRegister(char registerAddress, char value){
//Set Chip Select pin low to signal the beginning of an SPI packet.
digitalWrite(CS, LOW);
//Transfer the register address over SPI.
SPI.transfer(registerAddress);
//Transfer the desired register value over SPI.
SPI.transfer(value);
//Set the Chip Select pin high to signal the end of an SPI packet.
digitalWrite(CS, HIGH);
}
//This function will read a certain number of registers starting from a specified address and store their values in a buffer.
//Parameters:
// char registerAddress - The register addresse to start the read sequence from.
// int numBytes - The number of registers that should be read.
// char * values - A pointer to a buffer where the results of the operation should be stored.
void readRegister(char registerAddress, int numBytes, char * values){
//Since we're performing a read operation, the most significant bit of the register address should be set.
char address = 0x80 | registerAddress;
//If we're doing a multi-byte read, bit 6 needs to be set as well.
if(numBytes > 1)address = address | 0x40;
//Set the Chip select pin low to start an SPI packet.
digitalWrite(CS, LOW);
//Transfer the starting register address that needs to be read.
SPI.transfer(address);
//Continue to read registers until we've read the number specified, storing the results to the input buffer.
for(int i=0; i<numBytes; i++){
values[i] = SPI.transfer(0x00);
}
//Set the Chips Select pin high to end the SPI packet.
digitalWrite(CS, HIGH);
}
程式二:使用 I2C 連接
#include <Wire.h>
int I2C_Address = 0xA7 >> 1;
int X0, X1, Y0, Y1, Z1, Z0;
float X,Y,Z;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Start : \n");
Wire.begin();
setReg(0x2D, 0xA);
}
void loop(){
X0 = getData(0x32);
X1 = getData(0x33);
X = ((X1 << 8) + X0) / 256.0;
Y0 = getData(0x34);
Y1 = getData(0x35);
Y = ((Y1 << 8) + Y0) / 256.0;
Z0 = getData(0x36);
Z1 = getData(0x37);
Z = ((Z1 << 8) + Z0) / 256.0;
Serial.print("X= ");
Serial.print(X);
Serial.print(" Y= ");
Serial.print(Y);
Serial.print(" Z= ");
Serial.println(Z);
delay(500);
}
/* setReg(reg,data): */
void setReg(int reg, int data){
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_Address);
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.write(data);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
/* getData(reg): */
int getData(int reg){
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_Address);
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(I2C_Address,1);
if(Wire.available()<=1){
return Wire.read();
}
}